

These can be linked with branches on the remote, or they could exist with no remote counterpart.
When you run git branch -all, you will also see the local working branches. This is safe to do if you are using GitHub, because branches merged via pull requests can be restored. To delete the remote tracking branches that are deleted on the remote, run git fetch -prune. But, these will stack up over time - they are not deleted automatically. These don't take up much room, so it's okay that Git does this by default.
#Git add remote repo update#
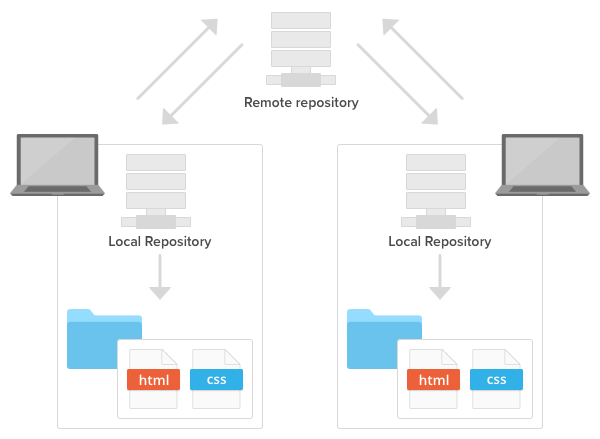
These update every time you run git fetch or git pull. These branches are read only copies of the branches on the remote. The branches that (by default) appear in red are the remote tracking branches. If you run git branch -all in your repository, you will notice a long list of branches. Git keeps track of the branches that you work on locally, as well as each of the branches in every remote associated with your local repo. The concept of branches can be confusing once it is combined with the concept of remotes. Unless you are using one of these four commands, all of your work is only happening locally. There are four commands within Git that prompt communication with the remote. It's typical to name this remote upstream. To make it easier to pull any changes to update the local copy of the fork from the original repository, many people add the original repository as a remote also. Then, the default remote would be origin, in reference to the fork. In this case, it's common to create and clone a fork. This can be common in open source, when a contributor needs to create a fork of a repository to have permission to push changes to the remote. You may need or want to work with multiple remotes for one local repository. It's like a key value pair, and origin is the default. origin is the human-friendly name for the URL that the remote repository is stored at. You may notice origin in many messages from Git. If you try running git remote -v in your repositories, you'll probably see something called origin. git remote -v: List the current remotes associated with the local repository.This kind of setup can be helpful if you're pulling in changes from the main branch of a project and then pushing any changes you make to a separate branch of your own, for example.Git remote manages the set of remotes that you are tracking with your local repository. This can be done with the following commands: $ git remote set-url $ git remote set-url -push This means you can actually set two different remote repositories for "origin", one for the push operation and one for fetch. In the output of the last command you may have noticed that there are actually two lines listed for the "origin" remote repository. Once you've added a remote to your repo you can then verify it with the -v flag: $ git remote -v You can also set these remotes as your default push or pull locations, shortening your Git commands even more.įor example, to add a remote origin to your repository, you would use the command like this: $ git remote add origin :scottwrobinson/camo.git The remote name is helpful for being able to reference this repository without having to type out the entire location.

The command you'll want to use is git remote add, and is generally used in the following way: $ git remote add
#Git add remote repo how to#
In this short article I'll explain exactly how to do that. Either way, it's beneficial to associate a remote repository to your local one. Or you may just want to have a way to link your local Git repo with the remote one on GitHub. This is beneficial for when you want to pull in updates from someone else's fork of a project, for example.
#Git add remote repo code#
In the Git version control system you're able to push and pull code from any number of remote repositories.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
